Drone (UAV) and its Classification - Based on Configuration
October 1, 2020 in Aerospace, Drones by ![]() Dhulkarnayn—4 minutes
Dhulkarnayn—4 minutes
In the contemporary world, the term drones is frequently mentioned everywhere. Their use across multiple industries like agriculture, cinema, tourism, and defence is steadily growing. Their increasing application suggests that this technology is poised to revolutionize numerous fields in the coming years.
What is a Drone?
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without a human pilot on board. The flight of drone is either controlled autonomously by computers in the vehicle or remotely controlled by a pilot on the ground.
Image Credits: Technology illustrations by Storyset
In simple terms, imagine a drone as a cool flying robot. Sometimes, this robot flies all by itself because it has a smart computer inside that tells it where to go, like a brain making decisions. Other times, a person on the ground uses a special remote control, like a video game controller, to guide the drone and make it fly where they want.
Classification of UAV
The UAVs/drones are classified into three types based on their design configuration, as listed below:
Did you know?
Often, we commonly label Rotary-Wing UAVs as drones, but technically speaking, all these types fall under the category of drones.
Fixed-Wing UAV
Fixed-wing UAVs resemble traditional airplanes but operate without an onboard pilot. They are primarily designed for specialized tasks like reconnaissance, surveillance, and spraying pesticides, among other specific missions.
Fixed-wing UAVs are typically preferred for missions that require long-range capabilities and extended endurance.

Image Credits: Lt. Col. Leslie Pratt / Public Domain
The image above showcases the General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, an American Fixed-wing UAV manufactured by General Atomics and predominantly utilized by the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
Rotary-Wing UAV
The rotary-wing UAV, also known as a rotorcraft, differs significantly from the previously mentioned structures. Its rotating wings, fixed within the vehicle’s frame, generate the lift needed for flight. These rotorcraft UAVs are typically favored for medium-range missions.
The rotary-wing UAV can be further categorized into two types:
Single-Rotor Vehicles
In single-rotor UAVs, the main rotor creates the lift needed for flight, while an extra vertical rotor helps steer the vehicle in the desired direction. A standout example of this type is the Single-Rotor Helicopter.
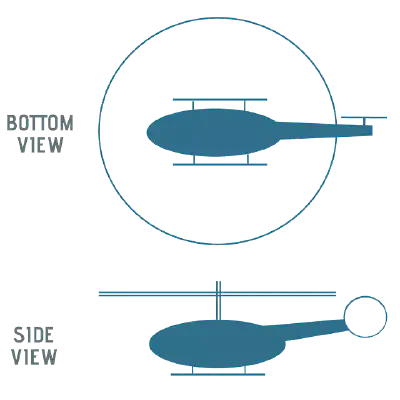
Image Credits: Austin, Reg. Unmanned Air Systems: UAV Design, Development and Deployment. 1st ed., Wiley, 20101
But when it comes to controlling the Single-Rotor Helicopter, it’s quite complex. It has its own advantages even though having complexity as compared to multirotor UAVs.
Multi-Rotor Vehicles
In the modern world of technology, when we mention UAVs or commonly called drones, we’re typically delving into a specific category. Within this category, there’s a fascinating array of designs and types.
For instance, you might come across terms like quadrotors, multirotors, octocopters, among others. Each of these configurations showcases the versatility and range of capabilities that drones bring to various fields and applications.

Image Credits: S. Hermann & F. Richter from Pixabay
The above image represents one of the successful commercial drones, DJI Mavic Pro which is most widely used in various fields such as tourism, cinema, etc.,
Hybrid UAV
Within the UAV landscape, the hybrid-wing UAV seamlessly merges features from two distinct categories: the Rotary-Wing UAV and the Fixed-Wing UAV.
What makes these hybrid models particularly intriguing is their capability for both vertical and horizontal takeoffs and landings, showcasing a versatile approach to flight operations.

Image Credits: Kyla Farmer, KindPNG
The image above showcases a hybrid-wing UAV designed for Vertical Take-off and Horizontal Transition (VTHT). Lately, hybrid UAVs have gained traction for their capability to undertake long-range and extended-duration missions.
Conclusion
Having explored the intricate landscape of drones and their classifications through a comprehensive analysis of various sources, I invite you to share your thoughts and feedback on this subject matter in the comments section below.
Knowledge is a collaborative journey, and I believe in the power of collective wisdom. If you found this article insightful, I encourage you to share it within your network. Your support and engagement are greatly appreciated. Thank you for taking the time to read and engage with this content!
This post is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0) by the author.
Please consider supporting this project!
If this article has been of help to you, and you feel generous at the moment, don’t hesitate to buy us a coffee. It's an easy, fun and direct way to show your support — any amount of coffee is highly appreciated.